Page 128 - Initial Public Offering - An Introduction to IPO on Wall Street
P. 128
In this section, we will discuss three main topics related to IPO costs: 1) the required resources
and their relative costs to account for during the IPO process; 2) The systemic improvements
and their relative costs that need to be made before and after an IPO; and 3) The appropriate
way to account for the discussed expenses.
6.1 The Costs
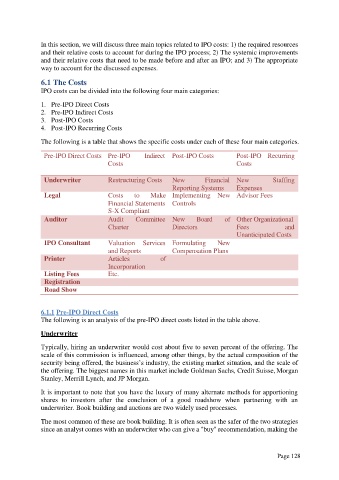
IPO costs can be divided into the following four main categories:
1. Pre-IPO Direct Costs
2. Pre-IPO Indirect Costs
3. Post-IPO Costs
4. Post-IPO Recurring Costs
The following is a table that shows the specific costs under each of these four main categories.
Pre-IPO Direct Costs Pre-IPO Indirect Post-IPO Costs Post-IPO Recurring
Costs Costs
Underwriter Restruc turing Costs New Financial New Staffing
Reporting Systems Expenses
Legal Costs to Make Implementing New Advisor Fees
Financial Statements Controls
S-X Compliant
Auditor Audit Committee New Board of Other Organizational
Charter Directors Fees and
Unanticipated Costs
IPO Consultant Valuation Services Formulating New
and Reports Compensation Plans
Printer Articles of
Incorporation
Listing Fees Etc.
Registration
Road Show
6.1.1 Pre-IPO Direct Costs
The following is an analysis of the pre-IPO direct costs listed in the table above.
Underwriter
Typically, hiring an underwriter would cost about five to seven percent of the offering. The
scale of this commission is influenced, among other things, by the actual composition of the
security being offered, the business’s industry, the existing market situation, and the scale of
the offering. The biggest names in this market include Goldman Sachs, Credit Suisse, Morgan
Stanley, Merrill Lynch, and JP Morgan.
It is important to note that you have the luxury of many alternate methods for apportioning
shares to investors after the conclusion of a good roadshow when partnering with an
underwriter. Book building and auctions are two widely used processes.
The most common of these are book building. It is often seen as the safer of the two strategies
since an analyst comes with an underwriter who can give a "buy" recommendation, making the
Page 128