Page 136 - Initial Public Offering - An Introduction to IPO on Wall Street
P. 136
6.1.6 Accounting for the Costs of an IPO
The Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") of the Financial Accounting Standards Board
("FASB") divides the expense guidelines mentioned above into two distinct parts. The actual
costs of the offering are covered by ASC 340-10-S99-1 (SAB Topic 5.A), while ASC 720-15
includes only those costs that classify as start-up expenditures.
ASC 340-10-S99-1 says that "specific incremental expenses specifically related to the planned
or actual offer of securities may be duly postponed and billed against the gross proceeds of the
offer."
The remaining expenses, on the other hand, come under the instructions found in ASC 720-15
and must be billed as incurred. The costs can be organized as follows, using the guidelines
found in the codification and the explanation in the PwC article:
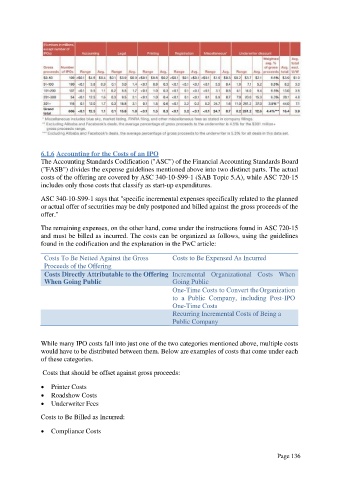
Costs To Be Netted Against the Gross Costs to Be Expensed As Incurred
Proceeds of the Offering
Costs Directly Attributable to the Offering Incremental Organizational Costs When
When Going Public Going Public
One-Time Costs to Convert the Organization
to a Public Company, including Post-IPO
One-Time Costs
Recurring Incremental Costs of Being a
Public Company
While many IPO costs fall into just one of the two categories mentioned above, multiple costs
would have to be distributed between them. Below are examples of costs that come under each
of these categories.
Costs that should be offset against gross proceeds:
Printer Costs
Roadshow Costs
Underwriter Fees
Costs to Be Billed as Incurred:
Compliance Costs
Page 136